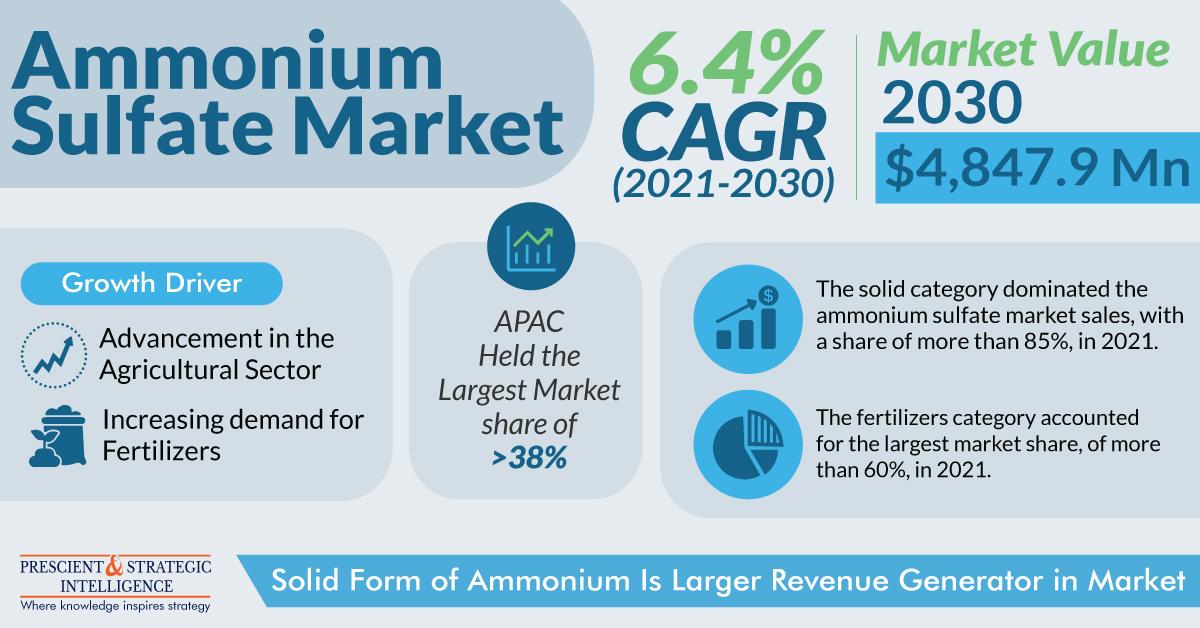
The ammonium sulfate industry has captured $2,775.7 million revenue, and it is projected to generate $4,847.9 million revenue in 2030, advancing at a rate of 6.4% in the coming years. The industry is transforming and constantly evolving, with surging enterprises operating in a global ecosystem to propel the industry intensity.
Technological advancement in the end-use sectors such as the geographical expansion of companies, process innovations, and rising manufacturing capabilities to offer larger industry space, are projected to proliferate the industry in near future.
The growing reliance of the global farming community on numerous agricultural inputs, including pesticides and fertilizers has resulted in the growing usage of nitrogenous fertilizers.
Almost, nothing can replace ammonium sulfate in agricultural fertilizer applications in the industry. That is why, the rising application has been limited to specific crops such as maize, soybean, and therefore it is least likely to find a substitute.
Furthermore, the bargaining power of suppliers is moderate in the industry which results in the forward integration of operations of most feedstock suppliers, such as ammonia, and sulfuric acid suppliers, with their strong presence in the agriculture sector.
The low-cost availability of raw materials such as ammonia and sulfuric acid across major agrarian countries such as MEA, APAC, and LATAM offers advantages to ammonium sulfate producers. Due to the high potential in these regions, corporations are massively investing in enhancing the production and manufacturing capacities through separate companies or partnerships, to remain competitive in the industry.
The solid category holds the largest industry share, of over 85% share. It is due to their potential to enhance the sulfur deficit and soil nutrient content. Solid ammonium sulfate crystals are worldwide used as fertilizers in alkaline soils. It enhances crop quality and yield.