Belly fat, also known as visceral fat, is more than just an aesthetic concern. It can pose serious health risks, particularly when it comes to metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. In this article, we will explore what is the strongest belly fat burner OTC and the connection between belly fat and metabolic syndrome, understand the underlying mechanisms, and discuss strategies to reduce this risk.
Understanding Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is not a single disease but rather a combination of several health conditions. To be diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, an individual typically exhibits three or more of the following factors:
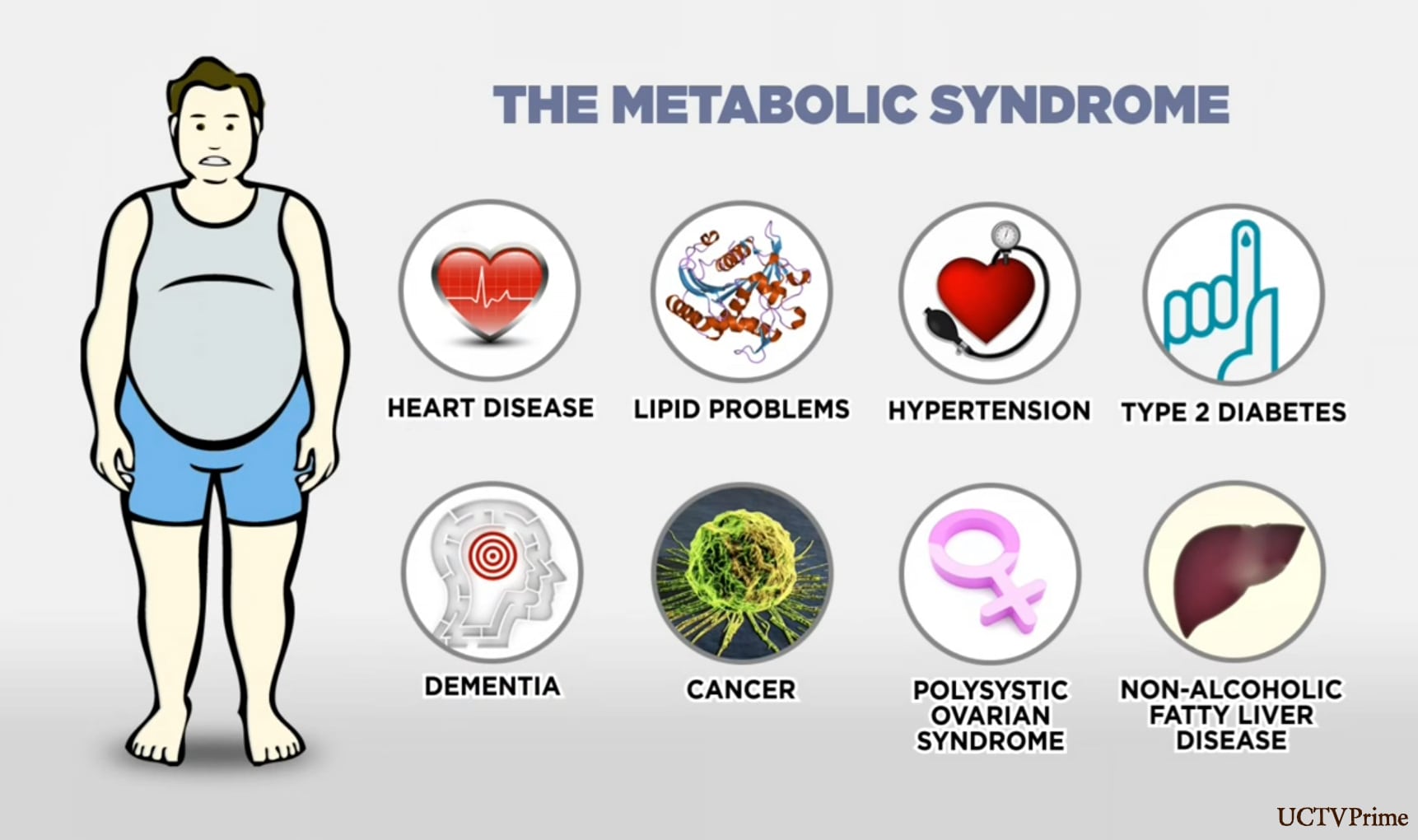
Abdominal Obesity: Excess fat around the waistline, commonly referred to as belly fat or visceral fat, is a key component of metabolic syndrome. It is measured by waist circumference and indicates a higher risk of metabolic disturbances.
High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure, or hypertension, is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. It is often associated with metabolic syndrome.
High Blood Sugar: Individuals with metabolic syndrome often have high blood sugar levels, which can lead to insulin resistance and, eventually, type 2 diabetes.
High Triglycerides: High levels of triglycerides, a type of fat in the blood, are another hallmark of metabolic syndrome.
Low HDL Cholesterol: Low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "good" cholesterol, are common in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
The Connection Between Belly Fat and Metabolic Syndrome
Belly fat is not just a passive storage site for excess energy; it is an active organ that releases hormones and inflammatory substances into the bloodstream. This activity can disrupt the body's normal functioning and lead to metabolic syndrome in the following ways:
Insulin Resistance: Visceral fat produces chemicals called adipokines that can interfere with insulin's ability to regulate blood sugar. This can lead to insulin resistance, a major precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Inflammation: Belly fat burner supplement is a source of chronic low-grade inflammation. This inflammation can impair blood vessel function, increase blood pressure, and promote the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
Fatty Liver: Excess visceral fat is associated with the accumulation of fat in the liver, a condition known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD is closely linked to metabolic syndrome.
Dyslipidemia: Visceral fat promotes changes in lipid metabolism, leading to elevated triglycerides and reduced HDL cholesterol levels, both characteristics of metabolic syndrome.
Reducing Belly Fat to Prevent Metabolic Syndrome
While genetics can play a role in where your body stores fat, lifestyle factors are key in reducing belly fat and lowering the risk of metabolic syndrome. Here are some strategies to consider:
Dietary Changes: Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive calories.
Regular Exercise: Engage in both cardiovascular exercises (e.g., running, cycling) and strength training (e.g., weightlifting) to burn calories and build muscle. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. Use smaller plates and utensils, and pay attention to hunger cues to stop eating when you're satisfied, not overly full.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to weight gain and belly fat supplements. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep can disrupt hormones related to hunger and appetite, leading to weight gain.
Alcohol Moderation: Limit alcohol consumption, as excess alcohol can contribute to abdominal obesity.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated, which can help control appetite and support metabolism.
Avoid Sugary Beverages: Sugary drinks like soda are a significant source of empty calories and can contribute to weight gain.
Regular Health Check-ups: Regularly monitor your blood pressure, blood sugar, and lipid profiles. Early detection and management of any abnormalities can help prevent the progression to metabolic syndrome.
Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you are struggling to lose belly fat with pills or manage your metabolic risk factors, consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support.
Conclusion
Belly fat burner supplement (https://www.outlookindia.com/outlook-spotlight/fast-weight-loss-pills-in-2023-top-5-diet-supplements-guaranteed-to-work-news-269969) is not just a cosmetic concern; it is a major contributor to metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Understanding the connection between belly fat and metabolic syndrome underscores the importance of adopting a healthy lifestyle. By making dietary changes, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and seeking professional guidance when needed, individuals can reduce belly fat and lower their risk of metabolic syndrome, ultimately leading to a healthier and longer life.
